The use of RFID offers many benefits to the healthcare industry related to patient safety, tracking, efficiencies in patient care, and provider satisfaction. Research shows that RFID can help to improve patient safety. RFID tags provide the ability to reduce misidentification issues in healthcare.
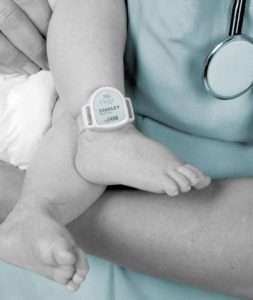
Accurate patient tracking using RFID technology can improve patient safety in many instances monitoring was effective in monitoring patients and equipment. Threshold monitors placed in 20 locations were found to have a 100% accuracy rate when detecting an event with an immediate notification on the application. It was acknowledged that this technology could have utility when tracking wandering patients with elopement risk, particularly with patients who suffer from Alzheimer’s and dementia. In the realm of newborn monitoring, RFID is being utilized to aid in the matching of newborns to their mothers and abduction prevention purposes. One RFID system utilized in a North Carolina hospital was effectively able to notify staff of infant abduction, allowing immediate intervention and recovery of the newborn.Healthcare, as an industry, is becoming more and more invested in RFID technology; so much so, that recent market research has revealed there will be exponential growth of RFID technology in that industry by 2021. One of the reasons that RFID is expanding considerably in the industry is the sheer number of applications that can benefit. In hospitals that have been outfitted with the technology, RFID is present in many forms – from tracking of surgical tools to tracking patients and staff.
Tracking inventory with RFID can be achieved with almost any types of item, but, RFID systems can be particularly challenging to implement when tracking liquid-filled assets. RFID tags with the ability to track these assets are becoming more readily available, largely due to the demand from the pharmaceuticals.
Hospitals have an ever-growing and changing supply of medicine that must be tracked in order to keep plenty on hand for their patients. Typical inventory tracking solutions (as with many industries) involve manual counts and barcodes which takes time for staff members to complete. Using RFID can reduce the amount of time spent counting, allowing pharmaceuticals to be counted more often, ensuring accurate data and that the correct types and amounts of drugs are on hand. RFID tags inside or on each bottle or box can be read with handheld readers during the inventory process, or constantly inventoried through fixed readers and shelf antennas.
Some hospitals and pharmaceutical manufacturers also use RFID tags for authentication purposes. Counterfeiting is on the rise due to high costs frequently associated with prescription and life-saving medications; so, many companies have opted for using RFID as an authentication or anti-counterfeiting resource. This is accomplished by placing an RFID tag on or within a medicine bottle or box and encrypting it with specific information so that hospitals and pharmacies can be verify that the medicines they sell are authentic. Tamper-proof RFID labels are also used in these applications to ensure quality.
Currently, hospitals are using passive RFID technology as well as instances of active RFID to track patients and staff throughout hospitals.
Patients and staff are outfitted with RFID tags in hospitals primarily for three reasons:
1. To verify patient information.
2. Reduce wait times and bottlenecks.
3. To locate patients.
Passive RFID systems are frequently used for maintaining and verifying patient records on wristbands. These RFID wristbands have patient information printed on them, and patient records are stored on the tag’s chip or associated with the tag’s ID through a database. Information encoded on the wristband’s tag is an optimal way of identifying patients because it can help in emergency situations by ensuring patients are not given the wrong medication or sent to the wrong area in the hospital. Lives have been lost due to accidents where patients’ files were switched. Important information encoded on the wristband such as “Allergic to nuts” or “DOB 7/29/80” could play a critical role in the patient’s outcome.
Active RFID is used in a few different ways in hospitals, but mostly for applications involving tracking staff and patients. Recently, Hospitals have used active RFID in Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) to identify problems in their workflow, mainly in order to move patients in and out quicker and more efficiently. In these instances, patients and staff have RTLS badges and the system identifies how long they have been in certain areas and reports that data to the management team.
RTLS is also implemented to track newborn babies. Research shows that, between 1965 and May 2017, 135 infants have been stolen from healthcare facilities in the United States alone*. Infants are not just stolen from random places in the facility, but trusted areas like the mother’s room, the nursery, and the pediatric hall. In order to lower the risk of infant abduction, hospitals place RTLS tags on all infant’s legs in order to monitor and track each child. If a child ventures too close to an exit door, an alarm will sound and the door will lock.
